In an era dominated by digital data, the importance of secure storage and transmission cannot be overstated. Cloud storage has emerged as a pivotal solution, providing users with convenient access to their data from anywhere in the world. However, this convenience comes with its own set of challenges, primarily centered around the security of sensitive information stored in the cloud. Encryption has become a cornerstone in addressing these concerns, acting as a robust safeguard against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Contents
Understanding Encryption Cloud Storage

Encryption, at its core, is the process of converting plaintext data into ciphertext, rendering it indecipherable without the corresponding decryption key. In the realm of cloud storage, encryption serves as a comprehensive defense mechanism against various forms of cyber threats. Let’s delve deeper into the types of encryption employed in securing cloud-based data:
- Symmetric Encryption:
- In symmetric encryption, a single cryptographic key is used for both the encryption and decryption of data.
- The efficiency of symmetric encryption is notable, but it introduces challenges in securely distributing and managing the encryption key, especially in large-scale cloud environments.
- Asymmetric Encryption:
- Asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
- While addressing the key distribution challenge, asymmetric encryption is computationally more intensive. It often finds application in securing key exchange processes rather than encrypting entire datasets.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE):
- E2EE takes encryption a step further by ensuring that data is encrypted on the client device before transmission and can only be decrypted on the recipient’s device.
- This method guarantees that not even the cloud service provider has access to the unencrypted data, assuring users of the highest level of privacy and security.
Types of Encryption Cloud Storage
- Symmetric Encryption:
- In symmetric encryption, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption. This key must be securely shared between the parties involved.
- While efficient, managing and distributing keys securely can be challenging, especially in large-scale systems.
- Asymmetric Encryption:
- Asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
- This method eliminates the need to share a common key, enhancing security. However, asymmetric encryption is computationally more intensive.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE):
- E2EE ensures that data is encrypted on the client device and can only be decrypted on the recipient’s device.
- Even the service provider cannot access the decrypted data, providing an additional layer of security.
Encryption in Cloud Storage
- Data at Rest Encryption:
- Encrypting data while it is stored in the cloud is crucial. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information even if a breach occurs.
- Cloud service providers often implement robust encryption algorithms to protect data at rest.
- Data in Transit Encryption:
- Encrypting data during transmission between the client and the cloud server is equally vital.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are commonly used protocols to establish encrypted connections, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
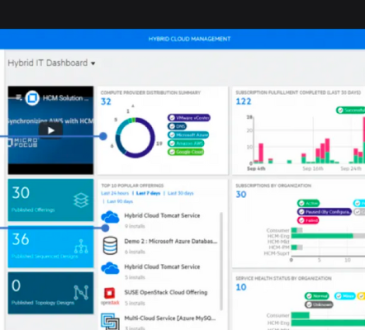
- Client-Side Encryption:
- Client-side encryption involves encrypting data on the user’s device before it is uploaded to the cloud.
- This approach provides an additional layer of security, as the cloud service provider only stores encrypted data, making it unreadable without the decryption key.
Challenges and Considerations
- Key Management:
- The secure management of cryptographic keys is a critical aspect of encryption. Losing keys or improper key storage can lead to data loss.
- Robust key management systems are essential to ensure the effectiveness of encryption.
- Performance Impact:
- Encryption and decryption processes can introduce computational overhead, impacting the performance of cloud storage systems.
- Optimizing encryption algorithms and utilizing hardware acceleration can help mitigate this challenge.
- Compliance and Regulations:
- Various industries and regions have specific data protection regulations. Ensuring that encryption practices align with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal repercussions.
- User Experience:
- Striking a balance between security and user experience is vital. Complex encryption processes should not hinder the usability of cloud storage platforms.
Benefits of Encryption Cloud Storage

- Confidentiality:
- Encryption ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access to the data, they cannot decipher it without the proper keys.
- Integrity:
- Data integrity is preserved through encryption, preventing tampering or unauthorized modifications during transmission or storage.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Adhering to encryption best practices aids in meeting regulatory requirements, which is crucial for businesses operating in various industries.
- Trust and Reputation:
- Implementing robust encryption measures enhances user trust, as clients feel more confident that their sensitive information is secure.
Conclusion
In the ever-expanding landscape of digital data, the security of information stored in the cloud is paramount. Encryption stands as a formidable defense against unauthorized access and data breaches, providing a secure environment for sensitive information. Cloud service providers, businesses, and individual users must prioritize the implementation of encryption protocols to safeguard their data and maintain the trust of their stakeholders. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of encryption methods will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of secure cloud storage.