In today’s digital age, businesses face increasing pressure to adopt cloud computing solutions that can enhance their agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Hybrid cloud environments have emerged as a promising solution, combining the best of both worlds by integrating private and public clouds. This article explores the concept of a hybrid cloud environment, its benefits, challenges, and best practices, empowering businesses to harness its power effectively.
Contents
Understanding the Hybrid Cloud Environment

A. Defining the hybrid cloud: The hybrid cloud environment refers to a seamless integration of public and private clouds, enabling businesses to store and process data across both environments.
B. Components of a hybrid cloud: Private cloud, public cloud, and the network bridge form the three essential components of a hybrid cloud environment.
C. Hybrid cloud architecture: Explore the architectural framework of a hybrid cloud, including infrastructure, data integration, security, and management.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Environment
A. Scalability and Flexibility: Hybrid cloud allows businesses to scale resources up or down according to their needs while providing the flexibility to choose the most suitable cloud environment for specific workloads.
B. Cost Optimization: By leveraging the hybrid cloud, organizations can optimize costs by efficiently allocating workloads based on their requirements and leveraging the cost advantages of public and private clouds.
C. Security and Compliance: Hybrid cloud environments offer enhanced security by allowing sensitive data to remain within the private cloud, while non-sensitive data can be stored in the public cloud. This segregation helps in maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
D. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Hybrid clouds enable businesses to implement robust disaster recovery and business continuity strategies by replicating critical data and applications across both public and private clouds.
Challenges and Considerations
A. Data Integration and Interoperability: Ensuring seamless data integration and interoperability between public and private clouds can be a complex challenge, requiring careful planning and implementation.
B. Security and Privacy Concerns: Organizations need to address security concerns associated with transferring data between public and private clouds, protecting data in transit, and implementing robust access control mechanisms.
C. Vendor Lock-In: Businesses must consider the potential for vendor lock-in when adopting a hybrid cloud environment, ensuring that they have the flexibility to switch providers or cloud models if required.
D. Performance and Latency: Optimizing performance and minimizing latency can be challenging when dealing with data transfers between public and private clouds, requiring efficient network configurations and caching strategies.
Best Practices for Implementing Hybrid Cloud

A. Assess Workload Requirements: Conduct a thorough assessment of workloads and data to determine the most suitable cloud environment and migration strategy.
B. Design for Interoperability: Plan for seamless data integration, implement standardized APIs, and ensure compatibility between public and private cloud platforms.
C. Security and Compliance Measures: Develop a comprehensive security strategy, including data encryption, access control, and compliance monitoring tools to protect data across both cloud environments.
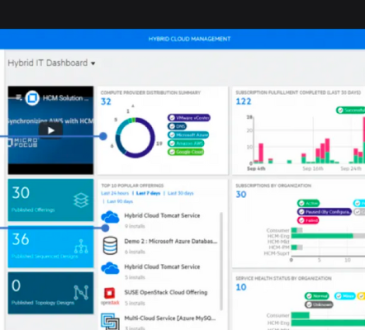
D. Hybrid Cloud Management: Implement robust management tools and frameworks to monitor, orchestrate, and optimize resources across the hybrid cloud environment.
E. Continual Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor and optimize the hybrid cloud environment to ensure efficient resource utilization, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Use Cases and Examples
A. E-commerce: Hybrid cloud environments are ideal for e-commerce businesses that experience fluctuating demand. They can leverage the scalability of public clouds during peak seasons while keeping sensitive customer data secure in the private cloud.
B. Healthcare: The healthcare industry benefits from hybrid cloud environments by securely storing and managing patient data in the private cloud, while leveraging public cloud services for research, collaboration, and data analytics.
C. Financial Services: Financial institutions can use hybrid cloud environments to comply with regulatory requirements by storing sensitive financial data in a private cloud, while utilizing the agility and cost efficiency of public clouds for non-sensitive operations.
D. Media and Entertainment: Hybrid cloud allows media companies to efficiently manage the storage and processing of large media files, while leveraging the public cloud for content distribution and streaming services.
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies Hybrid Cloud Environment

A. Edge Computing: Hybrid cloud environments are evolving to include edge computing capabilities, enabling businesses to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making.
B. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Hybrid cloud environments can leverage AI and ML technologies to analyze massive amounts of data stored across public and private clouds, enabling advanced insights and automation.
C. Containerization and Microservices: The adoption of containerization technologies and microservices architecture complements hybrid cloud environments, enabling businesses to develop and deploy applications more efficiently and scale them across multiple clouds.
D. Serverless Computing: Serverless computing models, such as Function-as-a-Service (FaaS), are gaining popularity in hybrid cloud environments, allowing businesses to execute code without the need to manage server infrastructure, optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs.
Conclusion
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, the hybrid cloud environment offers a powerful solution to meet their evolving needs. By combining the advantages of private and public clouds, organizations can achieve scalability, flexibility, cost optimization, security, and compliance. However, implementing a successful hybrid cloud environment requires careful planning, addressing challenges such as data integration, security, and vendor lock-in. By following best practices, continuously monitoring and optimizing the hybrid cloud environment, and exploring emerging technologies, businesses can unlock the full potential of hybrid cloud computing, driving innovation, and gaining a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
In conclusion, the hybrid cloud environment is a transformative approach that empowers businesses to leverage the benefits of both public and private clouds. By understanding its components, benefits, challenges, and best practices, organizations can make informed decisions, effectively implement hybrid cloud solutions, and reap the rewards of enhanced agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in their digital journey.