What Are The 4 Types of Cloud Storage? A Comprehensive Guide

In today’s digital era, data has become the lifeblood of organizations worldwide. As businesses strive to stay competitive and agile, the need for efficient and reliable storage solutions has never been more critical. Enter cloud storage – a paradigm-shifting technology that has revolutionized the way we store, manage, and access data. But not all cloud storage solutions are created equal. With Bubmbag, understanding the nuances of the four main types of cloud storage is essential for organizations to make informed decisions about their data management strategies. So, what are the 4 types of cloud storage?
Contents
What Are The 4 Types of Cloud Storage?
Public Cloud Storage: A Versatile Solution for Modern Businesses
The first type of cloud storage, as we delve into our exploration, is Public Cloud Storage. In this model, third-party service providers offer storage services over the internet, allowing users to store their data in remote servers accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. Public cloud storage providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offer scalable, pay-as-you-go storage solutions that cater to the diverse needs of businesses of all sizes.
One of the primary advantages of public cloud storage is its scalability. Organizations can easily scale their storage resources up or down based on their fluctuating needs, eliminating the need for costly infrastructure investments. Additionally, public cloud storage providers offer a wide range of services, including data backup, file sharing, and archival storage, making it a versatile solution for modern businesses.
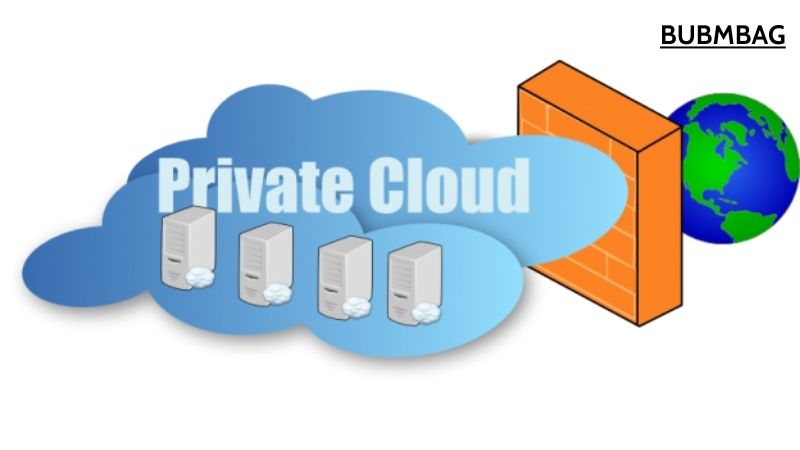
Private Cloud Storage: Elevating Security and Control
As we navigate through the cloud storage landscape, we encounter Private Cloud Storage. Unlike public cloud storage, which is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, private cloud storage involves storing data in a proprietary architecture dedicated to a single organization. This model offers greater control, security, and customization options, making it an ideal choice for organizations with stringent data privacy and compliance requirements.
Private cloud storage can be deployed on-premises within an organization’s data center or hosted by a third-party service provider. In either case, the organization retains full control over its data and infrastructure, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized access or breaches. While private cloud storage may require higher upfront investments compared to public cloud solutions, the long-term benefits of enhanced security and compliance make it a compelling option for many businesses.
Hybrid Cloud Storage: Finding the Perfect Balance
Continuing our exploration, we encounter Hybrid Cloud Storage – a hybrid approach that combines elements of both public and private cloud storage. In this model, organizations store sensitive data in a private cloud environment while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud storage for less sensitive data or fluctuating workloads. Hybrid cloud storage offers the flexibility to dynamically allocate resources based on changing business needs, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency.
The key advantage of hybrid cloud storage lies in its ability to strike the perfect balance between security and scalability. Organizations can maintain control over their most critical data while taking advantage of the agility and innovation offered by public cloud services. Additionally, hybrid cloud storage enables seamless data mobility, allowing organizations to move workloads between public and private clouds as needed, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing downtime.
Community Cloud Storage: Collaborating for Success
Our journey through the cloud storage landscape culminates with Community Cloud Storage – a collaborative approach where multiple organizations with similar interests share computing resources and storage infrastructure. Community cloud storage allows organizations within the same industry or sector to pool their resources, share costs, and leverage collective expertise while maintaining control over their data and operations.
Community cloud storage is particularly prevalent in sectors with stringent regulatory requirements or specialized needs, such as government agencies, healthcare organizations, and research institutions. By sharing infrastructure and resources, organizations can achieve economies of scale while ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. Additionally, community cloud storage fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing among participants, driving innovation and progress within the community.
Conclusion: Navigating the Cloud Storage Landscape
In conclusion, understanding the four types of cloud storage – Public Cloud Storage, Private Cloud Storage, Hybrid Cloud Storage, and Community Cloud Storage – is essential for organizations seeking to harness the power of cloud technology effectively. Each type offers unique advantages and considerations, allowing businesses to tailor their storage solutions to their specific needs, security requirements, and compliance mandates.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, organizations must carefully evaluate their storage options and adopt a strategic approach to cloud storage adoption. Whether it’s leveraging the scalability of public cloud storage, the security of private cloud storage, the flexibility of hybrid cloud storage, or the collaboration of community cloud storage, choosing the right model is key to unlocking the full potential of cloud technology and driving business success in the digital age. So, what are the 4 types of cloud storage? Understanding them is the first step towards a more efficient and resilient data management strategy.